VIRUS
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Virus is very much smaller than bacteria.
- It is an obligate parasite i.e. it can live only within the host.
- Both DNA and RNA act as a genetic material.
- Study of virus is known as virology.
- The body of virus is made up of lipids and proteins.
- Its body is known as viriods.
Structural properties:
- With the help of electron microscope, x-ray diffraction and some biochemical methods, structure of virus is studied.
- DNA of a virus is covered by capsid.
- Subunits of capsid are known as capsomeres. They are made up of proteins and are also known as proteomers.
Based upon structural properties, viruses are classified into four types:
i. Icosahedral shaped (20 equatorial triangles)
ii. Helical shaped (cylindrical)
iii. Complex shaped (tail, multilayer)
iv. Enveloped (spherical)
Icosahedral shaped virus:
- It is made up of 20 equatorial triangles.
- Outer layer is made up of capsid.
- In the corners, 5 protein subunits are present.
- In the center, 6 protein subunits are present.
- The protein subunits are known as capsomeres.
- Structure of capsomere is ring shaped.
- It consists of 252 capsomeres. Ex: Adenovirus, SV40.
HELICAL SHAPED VIRUS:
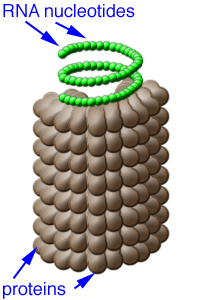
- It is a hollow tube shaped virus.
- Hollow tube is made up of proteins.
- Outer covering is known as capsid and is made up of proteins.
- Subunits of capsid are known as capsomeres.
- Diameter of TMV is 10 – 20 nm. 18 nm is occupied by capsomeres.
- Here, RNA acts as a genetic material.
- Generally RNA is helical, flexible and thin.
- Ex: TMV and Influenza virus.

- Ex: Teven phage l, T2, T4, bacteriophage.
- Icosahedral head is present.
- It consists of head, tail, tail pins, sheath and genetic material.
- Collar connects head to the helical sheath.
- Helical sheath is made up of complex proteins. It consists of several nucleotides, 24 rings, 18 proteins (144 copies).
- T1, T5 – Sheathless, base plate is absent.
- T3, T7 – No tail fibers.
- Tail pins contain some chemicals that can degrade cell wall of bacteria.
Enveloped virus:

- Ex: HIV virus, Influenza.
- Outer most layer of virus is called envelope.
- It consists of lipids and proteins.
- Lipid layer is derived from host cell.
- Protein is coded by gene.
- Generally, enveloped viruses have RNA as a genetic material.
- Spike is an external projection present on the envelope. It acts as a receptor for infection and binds to the host.
- They are known as spikes or paplomers.
- Spikes differ from species to species.
- Ex: 1. Haemoglutinin à recognize RBC wall and cause infection.
- 2. Neuraminidase spike à recognize mucous membrane of host.
- When enveloped viruses are treated with any solvents, spikes are easily degraded. Then it becomes non pathogenic.
- Diameter of virus is 10 nm.
- RNA dependent RNA polymerase is present in virus. Here, RNA is synthesized from RNA itself.
- Replicase, RNA transcriptase which are the enzymes necessary for the RNA synthesis are absent in virus. RNA dependent RNA polymerase is used for RNA synthesis.
- Polymerase enzyme undergoes proofreading and cleaves mismatch pairs.
- Infective portion of virus is known as viriods.


No comments:
Post a Comment